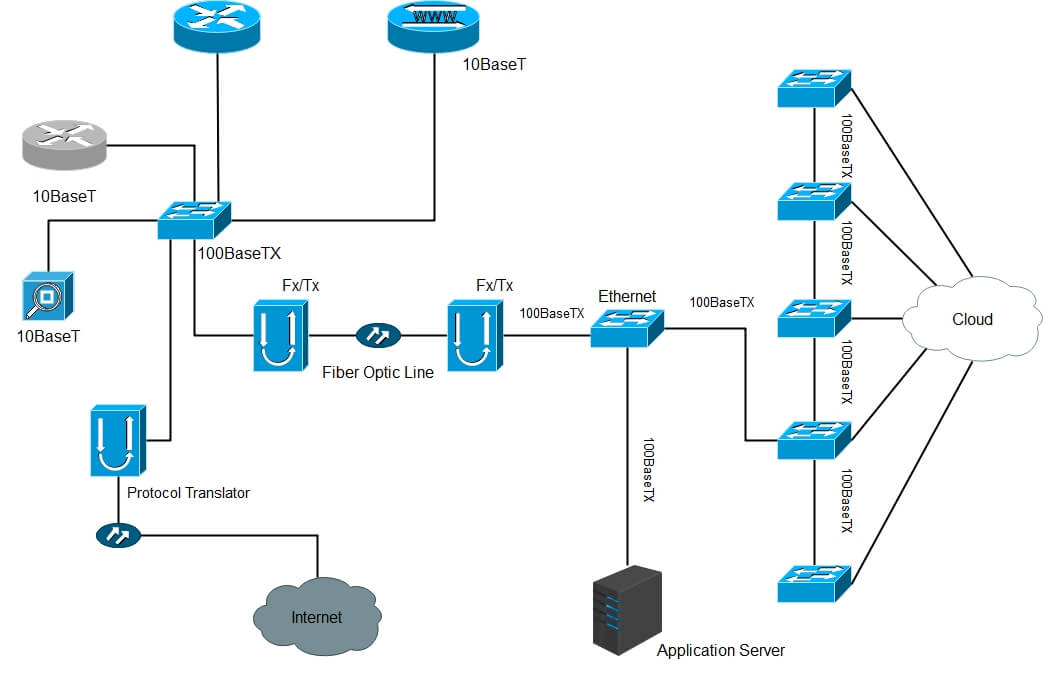
Network Topology
Contents
What is Network Topology?
The network topology is the arrangement of nodes and links in a particular mechanism and scheme. In other words, the network topology is how the network components that make the communication between the devices in a network would be arranged to reduce errors, produce more bandwidth speed, secure the network, etc.
The network topology diagram is shown in two ways. The logical network topology and the physical network topology.
The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals. Physical topology should not be confused with logical topology, which is used to pass information between work stations.
Topologies are of two types including physical topology and logical topology.
Physical topology is the arrangement of devices and other elements in a computer network. It includes the physical layout of nodes, computers, cables along with device location and code installation.
Logical topology is the way the logical flow of information in a network takes place. It is defined by the network protocol and dictates how data flows through the network. It is the arrangement of internal communication between devices.
A network consists of multiple computers connected using some interface. Each has one or more interface devices such as a Network Interface Card (NIC) and a serial device for PPP networking. Each computer is supported by network software that provides the server or client functionality. The hardware used to transmit data across the network is called the media. It may include copper cable, fiber optic, or wireless transmission. The standard cabling used for this document is the 10Base-T category 5 Ethernet cable. It is twisted copper cabling, which appears at the surface to look similar to TV coaxial cable. It is terminated on each end by a connector that looks much like a phone connector. Its maximum segment length is 100 meters.
In a server-based network, there are computers set up to be primary providers of services such as file service or mail service. The machines providing the service are called servers, and the computers that request and use the service are called client computers.
In a peer-to-peer network, various computers on the network can act both as clients and servers. For instance, many Microsoft Windows-based computers will allow file and print sharing. These computers can work both as clients and servers and are also referred to as peers. Many networks are a combination of peer-to-peer and server-based networks. The network operating system uses a network data protocol to communicate on the net to other computers. The network operating system supports the applications on that computer. A Network Operating System (NOS) includes Windows NT, Novell Netware, Linux, Unix, and others.
Main Types of Network Topologies
In networking, the term "topology" refers to the layout of connected devices on a network. There are several different types of network topology. One can think of a topology as a network's virtual shape or structure. This shape does not necessarily correspond to the actual physical layout of the devices on the network. For example, the computers on a home LAN may be arranged in a family room circle, but it would be highly unlikely to find an actual ring topology there.
Network topologies are categorized into the following basic types. And more complex networks can be built as hybrids of two or more of the underlying topologies.
1. Star Topology
Many home networks use star topology. A star network features a central connection point called a "hub" that may be a hub, switch, or router. Devices typically connect to the center with Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Ethernet. Compared to the bus topology, a star network generally requires more cable, but a failure in any star network cable will only take down one computer's network access and not the entire LAN. (If the hub fails, however, the whole network also fails.)
See the illustration of Star Network Topology.
Advantages of a Star Topology
- Easy to install and wire.
- No disruptions to the network were then connecting or removing devices.
- Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
- Centralization allows analysis of the traffic and straightforward detection of suspicious behavior.
- It is easy to expand, reconfigure and upgrade.
Disadvantages of a Star Topology
- It requires more cable length than a linear topology.
- If the hub or concentrator fails, the nodes attached are disabled.
- More expensive than linear bus topologies because of the cost of the concentrators.
- The speed and scale of the network depend on the hub configuration.
The protocols used with star configurations are usually Ethernet or LocalTalk. Token Ring uses a similar topology, called the star-wired ring.
Star-Wired Ring
A star-wired ring topology may appear (externally) to be the same as a star topology. Internally, the MAU of a star-wired ring contains wiring that allows information to pass from one device to another in a circle or ring (see fig. 3). The Token Ring protocol uses a star-wired ring topology.
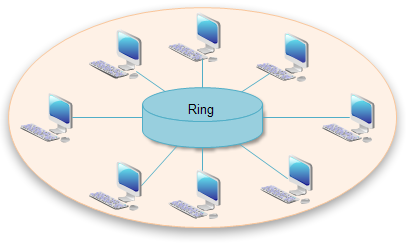
2. Ring Topology
In a ring network, every device has exactly two neighbors for communication purposes. All messages travel through a ring in the same direction (either "clockwise" or "counterclockwise"). A failure in any cable or device breaks the loop and can take down the entire network. To implement a ring network, one typically uses FDDI, SONET, or Token Ring technology. Ring topologies are found in some office buildings or school campuses.
See the illustration of Ring Topology.
Advantages of a Ring Topology
- Efficient management of data collisions because of the token system.
- Cost-efficient because less cable is utilized.
Disadvantages of a Ring Topology
- Difficult to troubleshoot.
- Expansion disturbs a large part of the network.
3. Bus Topology
Bus networks (not to be confused with the system bus of a computer) use a common backbone to connect all devices. A single cable, the backbone functions as a shared communication medium that devices attach or tap into with an interface connector. A device wanting to communicate with another device on the network sends a broadcast message onto the wire that all other devices see. Still, only the intended recipient accepts and processes the message.
Ethernet bus topologies are relatively easy to install and don't require much cabling compared to the alternatives. 10Base-2 ("ThinNet") and 10Base-5 ("ThickNet") both were popular Ethernet cabling options many years ago for bus topologies. However, bus networks work best with a limited number of devices. If more than a few dozen computers are added to a network bus, performance problems will likely result. Also, if the backbone cable fails, the entire network effectively becomes unusable.
See the illustration of Bus Network Topology.
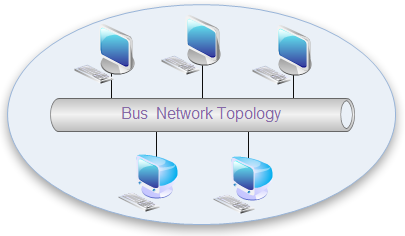
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology
- Easy to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus.
- It requires less cable length than a star topology.
Disadvantages of a Linear Bus Topology
- The entire network shuts down if there is a break in the main cable.
- Terminators are required at both ends of the backbone cable.
- Difficult to identify the problem if the entire network shuts down.
- Not meant to be used as a stand-alone solution in a large building.
- Data collisions are common if not managed.
4. Tree Topology
Tree topologies integrate multiple star topologies onto a bus. In its purest form, only hub devices connect directly to the tree bus, and each hub functions as the "root" of a tree of devices. This bus/star hybrid approach supports the network's future expandability much better than a bus (limited in the number of devices due to the broadcast traffic it generates) or a star (defined by the number of hub connection points) alone.
See the illustration of Tree Network Topology.
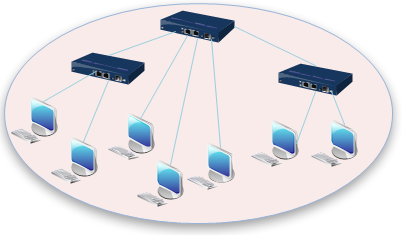
Advantages of a Tree Topology
- Easy scalability
- Troubleshooting is easier because each branch is independent.
- A large number of nodes can be connected.
- Point-to-point wiring for individual segments.
- Supported by hardware and software vendors.
- Minimal or no data loss.
Disadvantages of a Tree Topology
- The overall length of each segment is limited by the type of cabling used.
- All nodes are dependent on the central hub. If the backbone line breaks, the entire segment goes down.
- Tree topology is an expansive network layout. More difficult to configure and wire than other topologies.
5-4-3 Rule
A consideration in setting up a tree topology using Ethernet protocol is the 5-4-3 rule. One aspect of the Ethernet protocol requires that a signal sent out on the network cable reaches every part of the network within a specified time. Each concentrator or repeater that a message goes through adds a small amount of time. It leads to the rule that there can only be a maximum of 5 segments between any two nodes on the network, connected through 4 repeaters/concentrators. Also, only 3 of the parts may be populated (trunk) segments if they are made of coaxial cable. A populated section is one that has one or more nodes attached to it. In Figure 4, the 5-4-3 rule adheres to each other. The furthest two nodes on the network have four segments and three repeaters/concentrators between them.
This rule does not apply to other network protocols or Ethernet networks where all fiber optic cabling or a combination of a fiber backbone with UTP cabling is used. If there is a combination of fiber optic backbone and UTP cabling, it is simply translated to 7-6-5 rule.
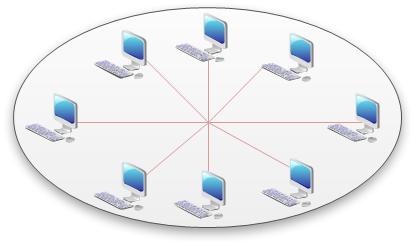
5. Mesh Topology
Mesh topologies involve the concept of routes. Unlike each of the previous topologies, messages sent on a mesh network can take any of several possible paths from source to destination. (Recall that even in a ring, although two cable paths exist, messages can only travel in one direction.) Some WANs, most notably the Internet, employ mesh routing.
A mesh network in which every device connects to every other is called a full mesh. As shown in the illustration below, partial mesh networks also exist in which some devices connect only indirectly to others.
The Mesh topology is further classified into two parts.
- Full Mesh topology
- Half Mesh topology
Full Mash topology
In a full mesh topology, the computers in a local area network are interconnected with every other computer in the same network.
Half Mesh topology
In a partial mesh topology, not all but few computers are interconnected with other computers to which they communicate constantly.
See the illustration of Mesh Network Topology.
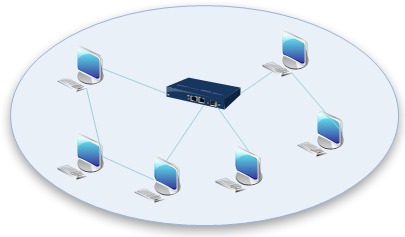
Advantages of a Mesh Topology
- It is a very stable system because a failure node cannot affect the rest of the work.
- Communication is very fast.
- No data collision.
- It is very private and secure.
Disadvantages of a Mesh Topology
- Very expensive because of extra cabling.
- Installation and maintenance are very complex.
6. Hybrid Topology
A combination of any two or more network topologies. Note 1: Instances can occur where two basic network topologies, when connected, can still retain the basic network character, and therefore not be a hybrid network. For example, a tree network connected to a tree network is still a tree network. Therefore, a hybrid network accrues only when two basic networks are connected, and the resulting network topology fails to meet one of the basic topology definitions. For example, two-star networks connected exhibit hybrid network topologies. Note 2: A hybrid topology always accrues when two different basic network topologies are connected.
Advantages of a Hybrid Topology
- These networks are very flexible and scalable.
- It can handle a large number of nodes.
- Less chance for data loss or collisions.
Disadvantages of a Hybrid Topology
- Multi-station access units (MSAU) are required.
- Expensive and complex to implement.
Importance of Network Topology
The network topology is essential because it makes the network more efficient. The exemplary network topology helps the network administrators to troubleshoot the errors and secure them more.
The network topology makes the transmission and receiving of data faster and secure as it increases the data efficiency. It simply leads to low-cost networks and that are easy to maintain.
Considerations When Choosing a Topology
Choosing the best topology is a critical decision for any network. The decision is based on many factors; however, the key is to fully understand the objectives and requirements. Also, the budget and the maintenance scale must be taken into consideration while making a decision. Remember to automate your network topology to make it secure and troubleshoot it automatically.
1. Length of cable needed
The length of the cable increases the network's cost and needs more effort in the installation of the network. If you want to use less cable, then the bus and star topologies are the best options. In comparison, mesh networks use a bigger volume of cable and are much more labor intensive.
Always see the hardware resources available to you. The best practice is that if you don't have the prerequisite hardware component for a particular topology, you should upgrade your components.
2. Cable type
You can either use coaxial cable, twisted pair, or fiber optic. Twisted pair cables are the least expensive but offer less bandwidth. At the same time, fiber optics provide the best performance in terms of speed but are fairly expensive. The choice of cable depends on the required performance level, budget, and the applications expected to run on the network.
3. Cost
The type of cable used, the amount of cable required, labor charges, and the setup cost all contribute to the network's cost. It would be best if you aimed for a balance between setup and the network's operational cost. Choose a network topology according to your business plan and services.
4. Scalability
Always pay attention to the application invocation patterns. If you expect the network to grow, aim for easily scalable network topology, like star topology. Ring networks are a no-no for any growing network. You can also choose a hybrid topology that allows nodes' addition without disturbing the rest of the network.
Always see the scalability requirements. Choose the topology that is easy to maintain. And select the more secure topology.
Network Topology Diagram Software
It is an easy-to-use and powerful topology diagram software with pre-made examples and symbols. It has become so easy to draw network topology diagrams, network mappings, home network diagrams, wireless network diagram, Cisco network topologies, network cable diagrams, logical network diagrams, network wiring diagrams, LAN network diagrams, activity network diagrams, etc. You can download Edraw Max and get started with its inbuilt examples.
EdrawMax
All-in-One Diagram Software
- Superior file compatibility: Import and export drawings to various file formats, such as Visio
- Cross-platform supported (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web)
How Network Diagram tools Help Manage and Monitor Networks?
A network topologies diagram explains a complicated network in a single screen. On the other hand, simply writing the description of the network makes it too complicated to follow. There are various tools available for drawing the network diagrams such as EdrawMax .
Other network tools allow the representation of security issues, pressure points, and management challenges. Automating the configuration and management of networks using the software tools releases a lot of pressure from the admins.
Let us discuss the most important uses of network tools.
1. Network Configuration
A network configuration tool helps to configure the network. You can also automate routine tasks using these tools. While managing smaller networks is straightforward. As the network expands, it becomes very complicated and time-consuming to keep the network running manually. A map is shown in the network configuration tools as a network topologies diagram that can detect where the problem has occurred. It makes troubleshooting rather easy.
These tools also support the network administrators to deploy standard configurations for compliance. Prediction and forecast is another very useful feature in network management tools. They can signal any potential vulnerability and the devices coming to the end of their life cycle.
2. Network Performance Troubleshooting
Network performance management has two aspects. One is monitoring, and the other is troubleshooting. A network needs to be monitored throughout its working hours to detect and fix any issue to minimize the outage time.
Network performance troubleshooting tools constantly monitor network issues along with outages and performance problems. You can define the parameters of performance, and when the network doesn't behave accordingly, the tool can issue a warning. This helps in the early detection and solution of issues.
How to Create a Network Topology Diagram?
Network topologies dictate the physical and logical layout of a network. Network diagram tool help manage and monitor networks by presenting the complete network in one diagram. How about create a network diagram yourself and see how it works? Find more details about how to create a network topology diagram.